hypothalamic pituitary axis|More : Manila Learn how the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland regulate endocrine responses to environmental changes. The web page explains the structure and function of the .
Resultado da dez 10 2021. Tendências e Prognósticos Para o Ano de 2022. Por Mapa Astral Védico em Artigos. No dia 15/12/2021 Marte encontra com Ketu, .
0 · hypothalamic pituitary growth hormone axis
1 · hypothalamic pituitary axis suppression
2 · hypothalamic pituitary axis function
3 · hypothalamic pituitary axis dysregulation
4 · hypothalamic pituitary axis dysfunction
5 · hypothalamic pituitary axis diagram
6 · explain hypothalamic pituitary thyroid axis and interrelationship
7 · cortisol is most dominant in the stress reaction i
8 · More
WEBPlayStation Vita is also known by many as PS Vita or simply as Vita. This is a gaming device manufactured by Sony, a famous company from Japan. In 2011, Sony was ranked as the fifth-largest electronics company in the .
hypothalamic pituitary axis*******The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis is a communication system between three organs. It’s crucial for your body’s stress management. These endocrine system organs create a feedback loop of hormones to enact and regulate your body’s .
A comprehensive overview of the anatomy, function, and hormones of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis, the coordinating center of the endocrine system. Learn .
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis is a system of hormones that regulates the stress response in the body. Learn how it works, what it does, an.The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA axis or HTPA axis) is a complex set of direct influences and feedback interactions among three components: the hypothalamus (a part of the brain located below the thalamus), the pituitary gland (a pea-shaped structure located below the hypothalamus), and the adrenal (also called "suprarenal") glands (small, conical organs on top of the kidneys). These organs The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA) is the main stress response system. It is the neuroendocrine link between perceived stress and physiological .
Learn how the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland regulate endocrine responses to environmental changes. The web page explains the structure and function of the . Learn how the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA axis) regulates stress responses, mood, digestion, immune function, and energy storage and expenditure in the body. Discover the role .
The Hypothalamic–Pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis describes a complex set of positive and negative feedback influences between the hypothalamus, pituitary .hypothalamic pituitary axis The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis is a key system that synchronizes the stress response with circadian regulatory processes. Regulation of the HPA axis is very dynamic with both .
In the HPA axis, the parvocellular neurosecretory cells release a hormone called corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) into a specialized capillary system that lies between the hypothalamus and the .
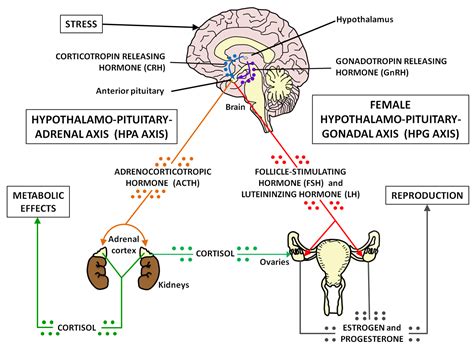
The hypothalamic pituitary axis is an intricate pathway with a central role in maintaining homeostasis by integrating complex physiological and endocrine inputs, and neuronal and hormonal output. Disorders of the pathway result in profound disturbance in blood pressure, thirst and electrolyte balance, body temperature, appetite and energy . The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis is a complex system of neuroendocrine pathways and feedback loops that function to maintain physiological homeostasis. Abnormal development of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis can further result in long-term alterations in neuropeptide and neurotransmitter synthesis .In the HPA axis, the parvocellular neurosecretory cells release a hormone called corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) into a specialized capillary system that lies between the hypothalamus and the pituitary called the .This collection of structures is commonly referred to as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis (Figure 1). In addition to the HPA axis, several other structures play important roles in the regulation of adaptive responses to stress. These include brain stem noradrenergic neurons, sympathetic andrenomedullary circuits, and . Disorders of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis can manifest in various clinical syndromes. Acromegaly and Pituitary Gigantism. Both acromegaly and pituitary gigantism are rare disorders of growth, occurring in anywhere between 40 to 125 per million people, that occur due to persistent secretion of growth hormone from the pituitary gland. . The activity of the thyroid gland is predominantly regulated by the concentration of the pituitary glycoprotein hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). In the absence of the pituitary or of thyrotroph function, hypothyroidism ensues. Thus, regulation of thyroid function in normal individuals is to a large extent determined by the . Endocrine system - Hypothalamic, Pituitary, Target Organs: The hypothalamic-pituitary-target organ axes of all vertebrates are similar. The hypothalamic neurosecretory system is poorly developed in the most primitive of the living Agnatha vertebrates, the hagfishes, but all of the basic rudiments are present in the . The HPA axis, or hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, is a complex set of interactions between the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and adrenal glands. It plays a critical role in regulating stress responses, mood, digestion, immune function, and energy storage and expenditure in the body. The pathway of the axis results in the production of . The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis is a complex system of neuroendocrine pathways and feedback loops that function to maintain physiological homeostasis. Abnormal development of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis can further result in long-term alterations in neuropeptide and neurotransmitter synthesis .hypothalamic pituitary axis More The hypothalamus is an endocrine organ located in the diencephalon of the brain. It receives input from the body and other brain areas and initiates endocrine responses to environmental changes. The hypothalamus acts as an endocrine organ, synthesizing hormones and transporting them along axons to the posterior pituitary gland.hide. The hypothalamic–pituitary–somatotropic axis ( HPS axis ), or hypothalamic–pituitary–somatic axis, also known as the hypothalamic–pituitary–growth axis, is a hypothalamic–pituitary axis which includes the secretion of growth hormone (GH; somatotropin) from the somatotropes of the pituitary gland into the circulation and . The somatotroph axis is composed by three different locations: hypothalamus, pituitary, and peripheral target organs. At hypothalamic level, the main peptides released to the hypophyseal blood are growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) with stimulatory action on pituitary hormonal release and somatostatin (SS) an .
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis is central to homeostasis, stress responses, energy metabolism, and neuropsychiatric function. The history of this complex system involves discovery of the relevant glands (adrenal, pituitary, hypothalamus), hormones (cortisol, corticotropin, corticotropin-releasing hormone), and the receptors for .

The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis describes a complex feedback system of neurohormones that are sent between the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and adrenal glands. This negative and positive feedback system regulates the physiological mechanisms of stress reactions, immunity, and fertility. . The HPA axis is meant to have a fine-tuned negative feedback loop: the cortisol in your body then triggers your hypothalamus to stop making CRH, ending the stress response. But experiencing frequent or intense stress and other issues can cause dysfunction with your HPA axis. The anatomy and unique blood supply of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis are essential to its function. The hypothalamic hormones are small peptides that are generally active only at the relatively high concentrations achieved in the pituitary portal blood system.More The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis involves the central nervous system and the endocrine system adjusting the balance of hormones in response to stress. Stress results in the hypothalamus stimulating the pituitary gland to release hormones that further cause the adrenal glands to release cortisol.The HPA axis, hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis, hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid (HPT) axis, and the hypothalamic–neurohypophyseal system are the four major neuroendocrine systems through which the hypothalamus and pituitary direct neuroendocrine function. One neuroendocrine system, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA), is crucial for stress management. Study of the HPA-axis illustrates a mélange of interactions between different physiological systems to ensure survival, longevity, development and homeostatic maintenance. The Hypothalamic–Pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis describes a complex set of positive and negative feedback influences between the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and adrenal gland.Describe the role of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis in the endocrine system. The hypothalamus in vertebrates integrates the endocrine and nervous systems. The hypothalamus is an endocrine organ located in the diencephalon of the brain. The HPA axis, or hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, is a complex set of interactions between the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and adrenal glands. It plays a critical role in regulating stress responses, mood, digestion, immune function, and energy storage and expenditure in the body.
Horns They are replacement 90MM Gen Yam looking horns .
hypothalamic pituitary axis|More